Accessibility means the ability to access products, services and other features of the environment by all people, irrespective of their age, ability or status in life. The concept is closely linked with the idea of Universal Design, coined by architect Ronald L. Mace, which propagates design that is aesthetic and is usable for all kinds of people.
Universal Design is the process of creating products that are usable by people with the widest possible range of abilities, operating within the widest possible range of situations. However, one significant work that pioneered the concept of free access to the disabled was that of Selwyn Goldsmith, author of Designing for the Disabled (1963). The concept emerged from barrier free design concepts, the broader accessibility movement and adaptive and assistive technology.
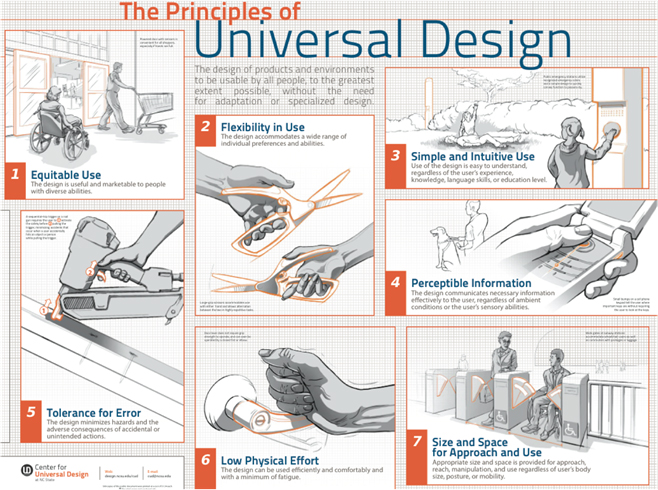
Source: Universal Design for Learning in HCPSS (udlhcpss.wordpress.com)
On December 3rd, 2015, also observed as ‘International Day for Persons with Disabilities’, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi launched the Accessible India Campaign. It is a programme that aims to make government buildings and public transportation disabled-friendly.
 Source: AccessibleIndia.gov.in
Source: AccessibleIndia.gov.in
Accessible India Campaign aims to achieve the following objectives:
- For Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) universal accessibility is critical for enabling them to gain access for equal opportunity and live independently and participate fully in all aspects of life in an inclusive society. Persons with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities, Protection of Rights and Full Participation) Act, 1995 under sections 44, 45 land 46 categorically provides for non-discrimination in transport, non-discrimination on the road and non-discrimination in built environment respectively. United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), to which India is a signatory, under Article 9 casts obligations on the Governments for ensuring to PwDs accessibility to
- Information,
- Transportation,
- Physical Environment,
- Communication Technology and
- Accessibility to Services as well as emergency services.
The Department hosted the Second Session of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) Working Group on Asian and Pacific Decade of Persons with Disabilities during 2-3 March, 2015 at New Delhi in association with the UNESCAP Secretariat. This Working Group has been constituted by UNESCAP Secretariat to monitor implementation of the Incheon Strategy “Make the Right Real” for Persons with Disabilities. Goal No. ‘3’ of Incheon Strategy concerns “Enhance access to the physical environment, public transportation, knowledge, information and communication”.
- It is the vision of the Government to have an inclusive society in which equal opportunities and access is provided for the growth and development of PwDs to lead productive, safe and dignified lives. In furtherance of the vision of the Department, it is imperative to launch a Nation-wide Awareness Campaign towards achieving universal accessibility for all citizens including PwDs in creating an enabling and barrier-free environment. In this direction, Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment has conceptualized the “Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan)”as a nation-wide flagship campaign for achieving universal accessibility that will enable persons with disabilities to gain access for equal opportunity and live independently and participate fully in all aspects of life in an inclusive society. The campaign targets at enhancing the accessibility of built environment, transport system and Information & Communication ecosystem.
- A multi-pronged strategy will be adopted for the campaign with key components as
(a) leadership endorsements of the campaign,
(b) mass awareness,
(c) capacity building through workshops,
(d) interventions (legal frame-work, technology solutions, resource generation, etc. and
(e) leverage corporate sector efforts in a Public-Private Partnership.
- Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities will sign MOU with State to support spreading awareness about accessibility and help create accessible buildings, accessible transport and accessible websites etc.
Information Resources:
A website dedicated to the Accessible India Campaign, hosted by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. The website aims to enhance large scale online participation of the public for the cause. It allows people to submit Accessibility Requests, for places that are inaccessible for persons with disabilities.
The paper talks about the governmental plans to follow up on successful implementation of the action plan for Accessible India Campaign. It outlines all the details of the steps that are planned to be taken in the coming months and year.
Guidelines intend to address the needs of persons with disabilities and elderly persons with a wide range of accessibility elements and standards and not limited to disabilities only, thus paving the way for universally accessible and inclusive India.
The manual has been developed by Samarthyam, New Delhi, for placing a framework of practice, to develop inclusive rights based on universally accessible sanitation designs. It is viable for institutional settings such as schools, public buildings and in emergency situations in both rural and urban areas.
This toolkit aims at assessing the current stage of inclusiveness and accessibility of PwDs in an organization and also acts as a guide for taking progressive steps to increase support, inclusiveness and accessibility towards persons / employees with disabilities. It is based on research, and the best examples and experiences of organisations that have taken initiatives to increase accessibility of PwDs and have benefited from such initiatives.
It talks about the status of people living with disabilities across the world and highlights the problems faced by them on a daily basis. It also talks about the solutions for these problems and suggests potential initiatives that can be undertaken by governments.
A collaboration between the Lebanese Government and United Nations led to the creation of this highly information guidelines that were framed to aid the government in making their country more inclusive and disabled-friendly. The guidelines can be used as a reference for the accessibility campaign in India
This is a set of guidelines to be followed as set by the WWW Consortium. It aims to help websites check their levels of compliance that are necessary to ensure that their content is accessible to people irrespective of their age, gender or capability.
References
Accessibility (June 4, 2016). Retrieved on June 22, 2016 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accessibility
Anonymous (2015). Accessible India Campaign: Creation of Accessible Environment for PwDs. Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India. Retrieved from http://disabilityaffairs.gov.in/content/accessible_india.php
Universal Design (June 14, 2016). Retrieved on June 22, 2016 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_design










